| Active substance | Azithromycin |
| US Brand | Zithromax, Azithrocin |
| IN Brand | Azee, Azicip |
| Manufacturing by | Cipla, India |
| Strength | 250mg, 500mg, 1000mg |
| Form release | Blister 1, or 5, or 6 pills |
| Estimated shipping time | 7 – 18 days (Depending from the Country) |
| Availability, Prices & Order | through request form |
Azithromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumonia, traveler’s diarrhea, and certain other intestinal infections. It may also be used for a number of sexually transmitted infections including chlamydia and gonorrhea infections. Along with other medications, it may also be used for malaria. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously with doses once per day.
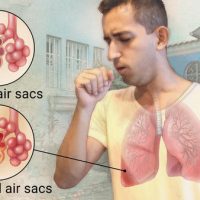
For bronchitis
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
Typical dosage is 500 mg once per day for three days. Your doctor may also prescribe 500 mg taken as a single dose on Day 1, followed by 250 mg once per day on Days 2–5.
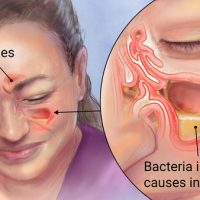
For sinusitis
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
Typical dosage is to take 500 mg once per day for three days.
Child dosage (ages 6 months–17 years)
Typical dosage is 10 mg/kg of body weight once per day for three days.
Child dosage (ages 0–6 months)
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
For skin and skin structure infections
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
Your doctor may prescribe 500 mg taken in a single dose on day 1, followed by 250 mg once per day on days 2–5.
Child dosage (ages 0–6 months)
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
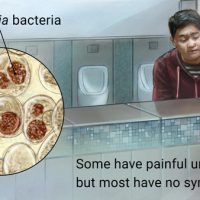
For urethritis and cervicitis
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
If your infection isn’t caused by gonorrhea, you’ll typically take a single 1-gram dose. If you are treating a symptom of a gonorrhea infection, you’ll typically take a single 2-gram dose.
Child dosage (ages 0–6 months)
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
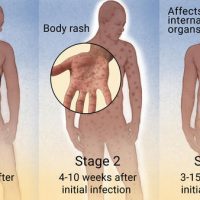
For genital ulcer disease
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
The doctor will typically prescribe a single 1-gram dose.
Child dosage (ages 0–6 months)
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
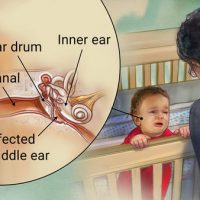
For acute middle ear infection
Child dosage (ages 6 months–17 years)
The typical dosage is 30 mg/kg of body weight taken as a single dose. The doctor may also prescribe 10 mg/kg of body weight on day 1, followed by 5 mg/kg per day on days 2–5.
Child dosage (ages 0–6 months)
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
For community-acquired pneumonia
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
Your doctor may prescribe 500 mg in a single dose on Day 1, followed by 250 mg once per day on Days 2–5.
Child dosage (ages 6 months–17 years)
Children of this age typically take 10 mg/kg of body weight in a single dose on day 1. Then they take 5 mg/kg once per day on days 2–5.
Child dosage (ages 0–6 months)
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
For mycobacterium avium complex disease
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
For treatment, typical dosage is 600 mg once per day, taken with the drug ethambutol.
For prevention, typical dosage is 1,200 mg once per week.
Child dosage (ages 0–6 months)
This drug should not be used in children who are younger than 6 months.
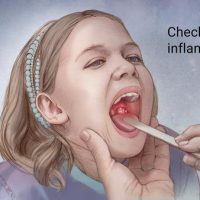
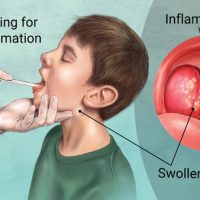
For pharyngitis or tonsillitis
Adult dosage (ages 18 years and older)
Your doctor may prescribe 500 mg in a single dose on day 1, followed by 250 mg once per day on days 2–5.
Child dosage (ages 2–17 years)
The typical dosage is 12 mg/kg of body weight once per day for five days.
Child dosage (ages 0–2 years)
This drug should not be used for this condition in children who are younger than 2 years.
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and upset stomach. An allergic reaction or a type of diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile is possible. No harm has been found with its use during pregnancy. Its safety during breastfeeding is not confirmed, but it is likely safe. Azithromycin is an azalide, a type of macrolide antibiotic. It works by decreasing the production of protein, thus stopping bacterial growth.